THERAPEUTICS
Small Molecule Inhibitors for QSOX1
20 QSOX1 inhibitors were identified from screening over 50,000 compounds in a high throughput screening assay. Several hit compounds are under investigation but one of them, SBI-183, was more active than others. SBI-183 demonstrated inhibitory activity in a concentration-dependent manner (bars 5-8 in the bar graph).
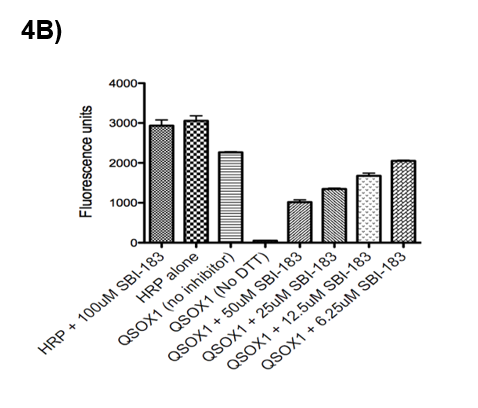
Figure 4B: Fluorogenic QSOX1 Activity Assay. Data were recorded at time = 15 minutes (steady state) after addition of substrate.
SBI-183 INHIBITS MIGRATION OF TUMOR CELLS IN 3D SPHEROID CULTURE
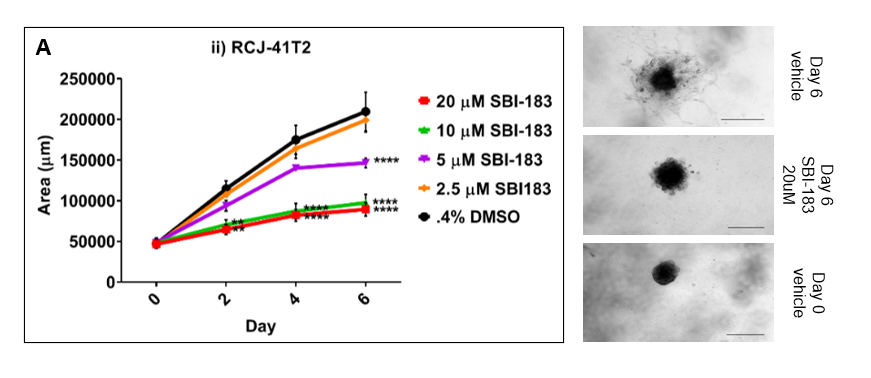
Figure 6A. SBI-183 inhibits migration of RCJ-41T2 sarcomatoid kidney cancer cells in Matrigel over 6 days. Line graph on left shows areas of 3D tumor spheroid at 0, 2, 4, and 6 days. Pictures of 3D RCJ-41T2 spheroids on right shows Day 6 DMSO vehicle (0.4%) on top, Day 6 20uM SBI-183 in middle and Day 0 spheroids on the bottom.
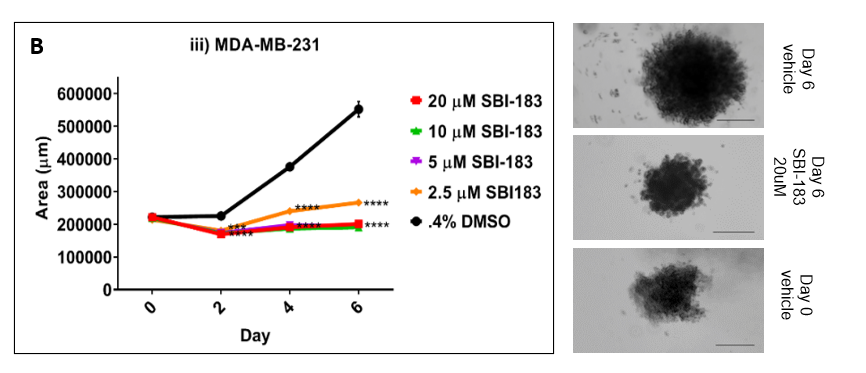
Figure 6B. SBI-183 inhibits migration of MDA-MB-231 TNBC cells in Matrigel over 6 days. Line graph on left shows areas of 3D tumor spheroid at 0, 2, 4, and 6 days. Pictures of 3D MDA-MB-231 tumor spheroids on right shows Day 6 DMSO vehicle (0.4%) on top, Day 6 20uM SBI-183 in middle and Day 0 spheroids on the bottom.
As shown in Figures 6A and 6B, SBI-183 inhibits the spread of tumor cells from 3D spheroids in Matrigel. In Figure 6A, Day 6 vehicle shows RCJ-41T2 tumor cells and tendrils of tumor cells spreading radially from the center of the spheroid (RCJ-41T2 is a primary tumor cell line derived from a patient at Mayo Clinic). MDA-MB-231 in Figure 6B grows faster than the RCJ-41T2 sarcomatoid kidney cancer in Figure 6A, but 20uM SBI-183 (middle panels in 6A and 6B) suppresses the radial spread of both tumor types. This result in similar to shRNA knockdown of QSOX1 in 786-O kidney cancer cells (data not shown, but published)[Hanavan, P.D. et al Oncotarget 2015].
IN VIVO ANIMAL STUDIES
In a human-xenograft mouse model, 786-0 renal cell carcinoma cells were implanted into the hind flanks of immunodeficient mice. Seven days after implantation, mice were treated with ~14 mg/kg per day by oral gavage. As shown in Figure 7A, tumors grew 86% more slowly in SBI-183-treated mice than vehicle-treated controls.
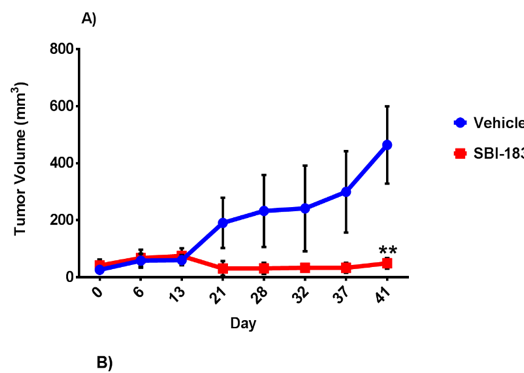
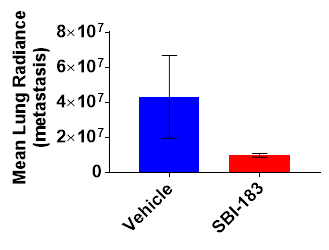
Figure 7A. Treatment of human tumor xenograft-bearing mice with SBI-183 suppresses tumor growth. Treatment was started on day 7 after tumor implantation. Experiment was terminated on day 41. Tumor volume, shown on the Y-axis was calculated using length and width measurements.
Figure 7B. Treatment of mice bearing MDA-MB-231-Luc tumors with 100mg/kg SBI-183, daily resulted in decreased lung metastasis in treated mice. Mice were injected with luciferin at the end of the experiment followed by ISIS 2000 imaging of lung mets and calculation of mean lung radiance using ISIS2000 software.
Since our hypothesis is that QSOX1 facilitates tumor invasion and metastasis, immunodeficient mice bearing triple negative breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-231-Luciferase expressing cells) were treated daily by oral gavage with SBI-183 for 28 days with 100 mg/kg dosage. Although there was no change in primary tumor size, lung metastases were reduced in treated vs control mice (Figure 7B). In a related experiment (data not shown), we determined that the maximal tolerated dose was >200 mg/kg SBI-183 and was limited by the solubility of the compound.